EvilNum is dangerous malware that targets financial and other organizations

EvilNum is a malicious piece of software designed to steal information and proliferate other malware

EvilNum is a malicious piece of software designed to steal information and proliferate other malware
EvilNum is a Trojan that was first discovered in 2018 and showed its appearances in subsequent years with new campaigns. Written in JavaScript code (although later versions used .NET), the malware is believed to be created and used by an unknown Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) group, which mainly targets financial businesses and organizations worldwide. While the operation of the virus is not complex, it allows the attackers to hide on the infected networks for a prolonged period of time and perform malicious operations in the background.
EvilNum virus is a well-developed data stealer which allows the attackers to execute commands remotely, take screenshots, proliferate other malware, capture login credentials, secret company documents, email contents, etc. Since its release, the malware has seen several upgrades by the attackers and was also used in many different campaigns, ranging from phishing emails to cloud-based links leading to a malicious payload. In 2019, researchers uncovered several similarities between EvilNum and Cardinal RAT, as companies have been submitting both samples at the same time.
| Name | EvilNum |
| Type | Trojan, info-stealer |
| Possible relations | Cardinal RAT |
| Programming language | Initial release was using JavaScript, while later versions were written in .NET |
| Capabilities |
|
| Distribution | Malicious links, macro-laced documents, exploits, spam emails, etc. |
| Removal | To terminate malware from the infected workstation, one has to first disconnect it from the infected network and then access Safe Mode with Networking to perform a full system scan with the most up-to-date security application |
| System fix | Malware can often damage various Windows components and corrupt system files. This damage can be easily fixed with repair software such as Reimage Reimage Cleaner Intego |
While EvilNum malware was previously analyzed several times, its newest campaign was spotted by Prevailion security researchers in May of 2020, who discovered two new campaigns (they named them “Phantom in the [Command] Shell”) targeting financial organizations:[1]
The Phantom in the Command Shell campaign shows that the threat actors behind the EVILNUM malware family are constantly advancing their techniques as they continue to focus their efforts on the global banking/financial system. The differences between the 3.6 and 4.0 variants appear to be trivial and do not affect functionality.
According to researchers, the malware is diverse and very adaptive, as it uses several different techniques to evade network and host detection. As soon as it enters the machine, it performs different actions depending on the installed anti-virus software (experts not that even different Command & Control servers might be utilized for particular workstations of networks). Due to this adaptive nature, EvilNum removal and detection might be difficult, as it also can remain on the network undetected.
However, the most up-to-date security applications should be able to remove EvilNum malware easily. However, it is very important to disconnect the infected machine from the network first, as the virus might easily reinfect it. We recommend using SpyHunter 5Combo Cleaner or Malwarebytes for the job and then employing Reimage Reimage Cleaner Intego to fix virus damage easily.
EvilNum is a Trojan that is used by an Advanced Persistence Treat group

EvilNum is a Trojan that is used by an Advanced Persistence Treat group
Before infecting the machine, the EvilNum virus would check the computername, username, and the installed antivirus product on the machine and would send off this information via the Command & Control[2] server to the attackers. Once executed, malware is capable of performing the following actions on the host machine:
- Take screenshots (although researchers mentioned that this function was missing from the latest version of malware)
- Steal cookies and other browser-related data
- Download and upload files from Command & Control server
- Install other malware
- Access otherwise restricted data/information
- Run arbitrary code, etc.
Palo Alto experts mentioned that, despite the fact that EvilNum can function on its own and evade detection well, it is usually used as an attack vector to proliferate other malware for main functionality:[3]
Despite this, the core functionality of the malware is mostly the same, and some of the concepts used in the malware family (such as the lock file) remain the same. It’s likely that the malware only serves as a first stage and the attackers deploy further tools to target networks of interest.
Deceptive infection tactics that abuse Windows .lnk files
The EvilNum attack begins when a victim receives a link that is hosted on well-known cloud services, such as Google Drive. These links are typically embedded within phishing emails that represent the corporate executives within the company so that the user would not suspect anything. Once the link is clicked, a compressed folder download starts. This technique is just another trick to evade detection of the infection, as detection systems do not check the integrity of files hosted on third-party sources.
Once the zip file is extracted, one of the following files will be delivered:
- Driv License front.jpg.lnk
- Driv License back.jpg.lnk
- Credit Card Front.jpg.lnk
- Credit Card Back.jpg.lnk
- Utility Bill.jpg.lnk.
As evident, these files are presented as a picture (.jpg), while researchers also uncovered others that are meant to seem like they are PDFs, while in reality, these are all Microsoft link files. Additionally, criminals employ social engineering to make users click on these files, as this information is commonly used by customers who are applying for financial services. Experts also saw differently named files that EvilNum extracts after the link are clicked – these often reference companies rather than individuals.
As soon as one of such link files are clicked, the infection routine begins, and the main payload is executed on the machine, ready to operate in the background.
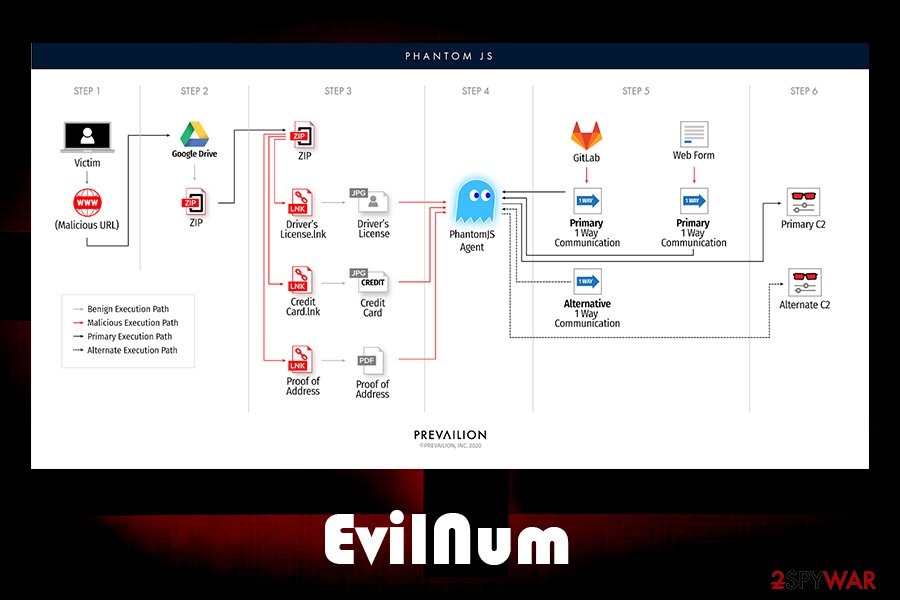
EvilNum infection begins with a victim downloading a malicious Zip file from Google Drive

EvilNum infection begins with a victim downloading a malicious Zip file from Google Drive
Social engineering tricks used to proliferate malware
Phishing emails are exceptionally dangerous, as they are the major attack vector when it comes to malware attacking businesses and organizations. While some emails can be recognized as fake immediately (lack of body text, visible grammar/spelling mistakes, inadequate formatting, etc.), some criminals, especially sophisticated APT groups put much effort to craft an email that looks legitimate and trustworthy.
Major email providers, such as Gmail or Outlook, use sophisticated malware scanners that mark these emails as malicious so that users can discard them immediately. However, some more advanced emails managed to bypass these security measures and end up in an Inbox instead of a Spam box.
In conjunction with evasion techniques, the attackers impersonate company officials and executives, making the email recipient not to think twice before opening the malicious attachment or clicking on an embedded hyperlink.
Quite often, documents with embedded macros are used. For the malware infection to begin, victims have to allow these macros to run on a .doc or .xlsm file (although other types can be used as well). Thus, these documents should never be allowed to run such commands in the first place, and a scan with anti-malware should be performed just to be sure.
Also, malicious actors now started employing malicious links that are hosted on a third-party cloud platform, such as Google Drive. In such a case, all security measures will fail if the individual will download the malicious files from the drive and click on relevant links.
EvilNum elimination methods
EvilNum virus is a highly evasive data-stealer which can also remain undetected by security software until the infection occurred. As a result, threat actors can remain connected to the connected network for weeks before being detected. In the meantime, more malware can be pushed via the initial attack vector, which can be EvilNum itself. Therefore, the first step when trying to protect the company network is to employ a sophisticated endpoint security solution suite. Also, the network should be constantly monitored for suspicious inbound connections to stop the intrusion immediately.
To remove EvilNum malware from the system, each of the infected computers should be first disconnected from the network. Then, the machine should undergo an extensive scan with the most up-to-date anti-malware software – a process that should be aided by the IT department.
Once EvilNum removal is complete, adequate measures should be taken to secure the network from future attacks of similar nature.
This entry was posted on 2020-05-22 at 09:10 and is filed under Malware, Viruses.

